
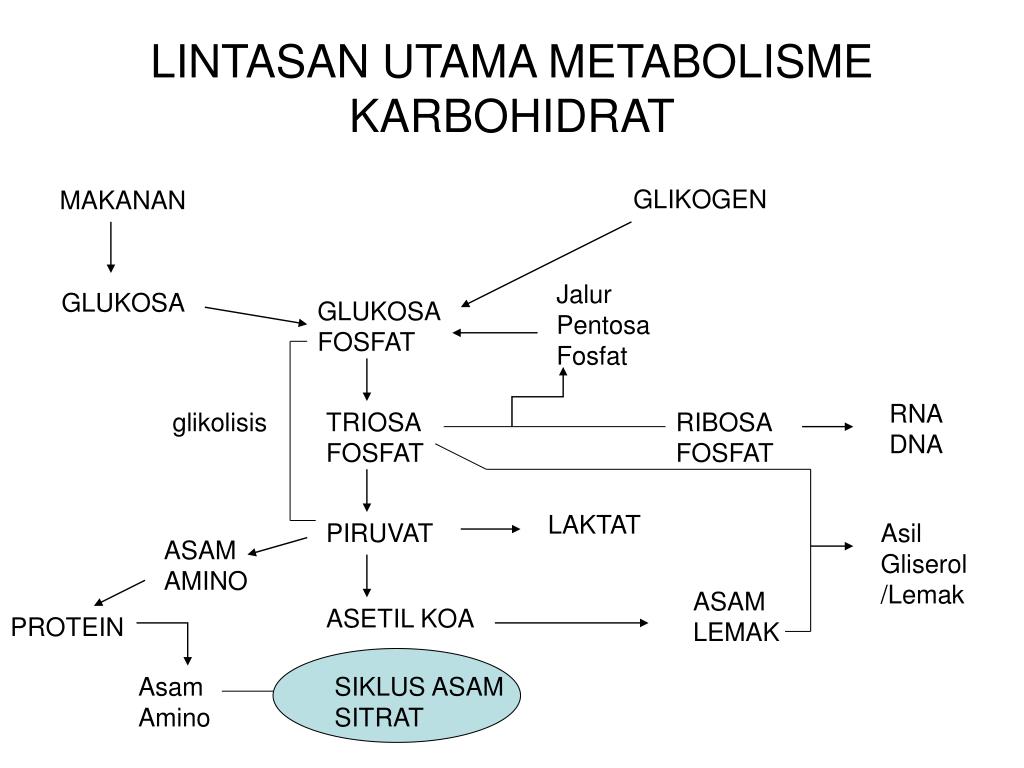

Nitrogenous waste disposal Ammonia (NH 3 ) very toxic carcinogenic very soluble easily crosses membranes must dilute it & get rid of it fast! How you get rid of nitrogenous wastes depends on who you are (evolutionary relationship) where you live (habitat) aquatic terrestrial terrestrial egg layer Intracellular Waste What waste products? Animals poison themselves from the inside by digesting proteins! what do we digest our food into carbohydrates = CHO CO 2 +H 2 O lipids = CHO CO 2 +H 2 O proteins = CHON CO 2 +H 2 O + N lots! nucleic acids = CHOPN CO 2 +H 2 O + P + N very little cellular digestion cellular waste NH 2 = ammonia H O H N C C OH H R CO 2 + H 2 O

Osmoregulation Water balance freshwater hypotonic water flow into cells & salt loss saltwater hypertonic water loss from cells land dry environment need to conserve water may also need to conserve salt hypotonic hypertonic Why do all land animals have to conserve water? always lose water (breathing & waste) AP may Biology lose life while searching for water Overcoming limitations of diffusion Evolution of exchange systems for distributing nutrients circulatory system removing wastes excretory system aa CO CO 2 2 NH NH 3 3 CO 2 NH 3 CO 2 CO 2 O 2 systems to support multicellular organisms O 2 aa CH NH 3 NH3 CO 2 CO 2 NH 3 NH 3 CO 2 CO 2 CO 2 NH 3 CHO aa Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007Īnimal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH aa CHO O 2 O 2 aa CO 2 NH 3 aa CH CHO O 2 aa CO 2 CO 2 NH 3 NH 3 CO 2 intracellular waste CO 2 NH 3 O 2 CO 2 O 2 aa NH 3 NH 3 NH3 CO 2 CO 2 NH 3 CO 2 CO 2 CO 2 NH 3 CHO CH aa Diffusion too slow! extracellular waste Homeostasis Keeping the balance animal body needs to coordinate many systems all at once temperature blood sugar levels energy production water balance & intracellular waste disposal nutrients ion balance cell growth maintaining a steady state condition

Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external environment allow internal conditions to fluctuate along with external changes thermoregulation osmoregulation regulator regulator conformer conformer Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007Ĭonformers vs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
